Kubernetes Cost Optimization: Taming Your K8s Cloud Spend
Kubernetes Cost Optimization: Taming Your K8s Cloud Spend
Running Kubernetes Can Get Expensive Fast. Optimize Your K8s Cloud Spend.
Kubernetes has become the de facto standard for orchestrating containerized applications, offering unparalleled scalability and flexibility. However, without careful management, the promise of efficiency can quickly turn into unexpectedly high cloud bills. For freelancers and small tech teams leveraging Kubernetes, understanding and implementing cost optimization strategies is crucial to avoid budget overruns.
Optimizing your Kubernetes costs isn't just about cutting corners; it's about intelligent resource utilization, right-sizing your clusters, and adopting best practices that ensure you get the most value from your cloud investment.
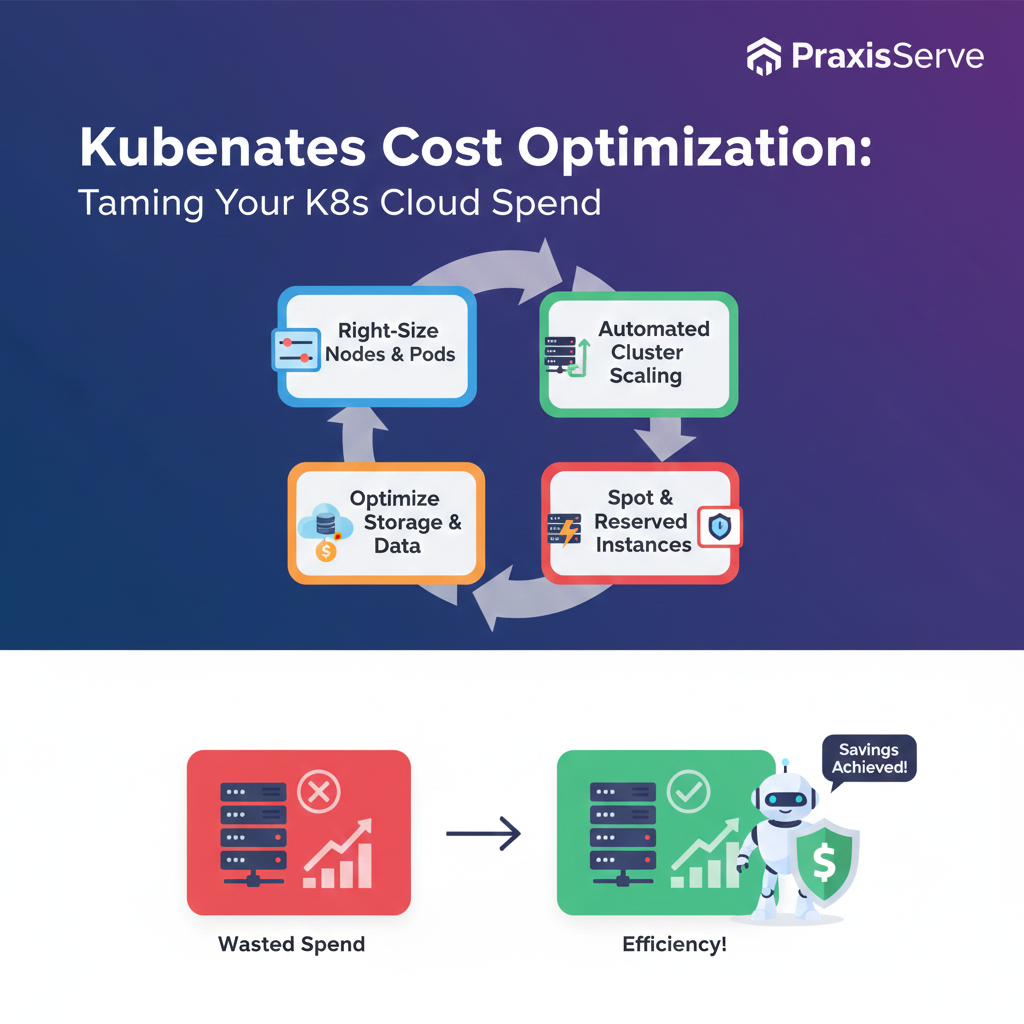
1. Right-Size Your Nodes & Pods
Over-provisioning is the quickest way to waste money in Kubernetes.
- Pod Resource Requests & Limits: Define accurate CPU and memory requests and limits for your pods. Requests ensure pods get the minimum needed, and limits prevent them from consuming excessive resources.
- Node Sizing: Choose instance types for your worker nodes that match your workload's actual requirements. Don't use large, expensive nodes if smaller ones suffice.
- Horizontal Pod Autoscaler (HPA): Configure HPA to automatically scale the number of pods up or down based on metrics like CPU utilization or custom metrics.
- Vertical Pod Autoscaler (VPA): VPA (in recommendation mode or auto-mode) can dynamically adjust the CPU and memory requests/limits for individual pods based on historical usage.
Key: Match resource allocation closely to actual demand.
2. Leverage Cluster Autoscaling
Beyond pod scaling, automatically scale your underlying worker nodes.
- Node Auto-Provisioning: Configure your Kubernetes cluster (EKS, AKS, GKE) to automatically add or remove worker nodes based on pending pods and resource utilization.
- Consolidate Workloads: Ensure your scheduler is configured to pack pods efficiently onto fewer nodes to maximize utilization before scaling up.
- Downscaling Policy: Fine-tune the downscaling policies of your cluster autoscaler to aggressively remove underutilized nodes after a period of low demand.
Benefit: Pay only for the node resources you actually need at any given moment.
3. Optimize Storage Costs
Persistent storage can be a hidden cost in Kubernetes.
- Choose Appropriate Storage Classes: Don't default to the highest-performance (and most expensive) storage for all Persistent Volumes (PVs). Match storage class to workload needs (e.g., standard HDD for logs, SSD for databases).
- Clean Up Unused PVs: Regularly audit and delete Persistent Volume Claims (PVCs) and PVs that are no longer in use, especially after deleting deployments.
- Object Storage for Static Assets: For static files and large binary data, leverage cost-effective object storage like S3, Azure Blob Storage, or GCS instead of block storage attached to nodes.
Tip: Automate storage cleanup where possible to prevent accrual of unused resources.
4. Use Spot Instances & Reserved Instances
Leverage cloud provider pricing models for significant savings.
- Spot Instances (for fault-tolerant workloads): Use spot instances for stateless, fault-tolerant workloads (e.g., batch jobs, development environments). Savings can be up to 90%, but instances can be reclaimed.
- Reserved Instances/Savings Plans (for stable workloads): For your base, stable Kubernetes workload, commit to Reserved Instances or Savings Plans for 1-3 years to get substantial discounts on compute capacity.
- Managed Services: Consider cloud-managed Kubernetes services (EKS, AKS, GKE) as they often handle master node costs and offer integrated cost tools.
Strategy: Combine these for a balanced approach: Spot for flexibility, Reserved for stability.
5. Monitor & Analyze Costs with Specialized Tools
You can't optimize what you can't measure.
- Cloud Billing Tools: Utilize native cloud cost explorers (AWS Cost Explorer, Azure Cost Management, GCP Cost Management) to track overall spend.
- Kubernetes Cost Management Tools: Implement specialized tools like Kubecost, OpenCost, or cloud provider add-ons (e.g., GKE Cost Optimization Hub) for granular, per-namespace/pod cost visibility.
- Anomaly Detection: Set up alerts for sudden spikes in Kubernetes-related cloud spend.
Continuous Improvement: Regularly review your cost reports and identify areas for further optimization.
Struggling with Kubernetes Costs? PraxisServe Can Help.
Managing Kubernetes costs effectively requires deep expertise in cloud architecture, cluster management, and financial operations. For freelancers and small teams, this can be a daunting challenge, often leading to wasted spend.
PraxisServe specializes in Kubernetes cost optimization. We'll help you audit your current setup, implement intelligent autoscaling, fine-tune resource allocations, and leverage the best pricing models, ensuring your K8s environment is efficient and budget-friendly.
Need Help with This?
Our team is ready to assist you with implementation and support.