Shifting Left: Integrating Security Early in the Development Lifecycle
Shifting Left: Integrating Security Early in the Development Lifecycle
Save Time, Reduce Risks, and Build More Robust Applications.
For many freelancers and small tech teams, security can often feel like an afterthought – something to worry about right before a big launch or, worse, after a vulnerability has been discovered. This approach, however, is a recipe for disaster. Fixing security flaws late in the development cycle, or in production, is exponentially more expensive and damaging than addressing them early on.
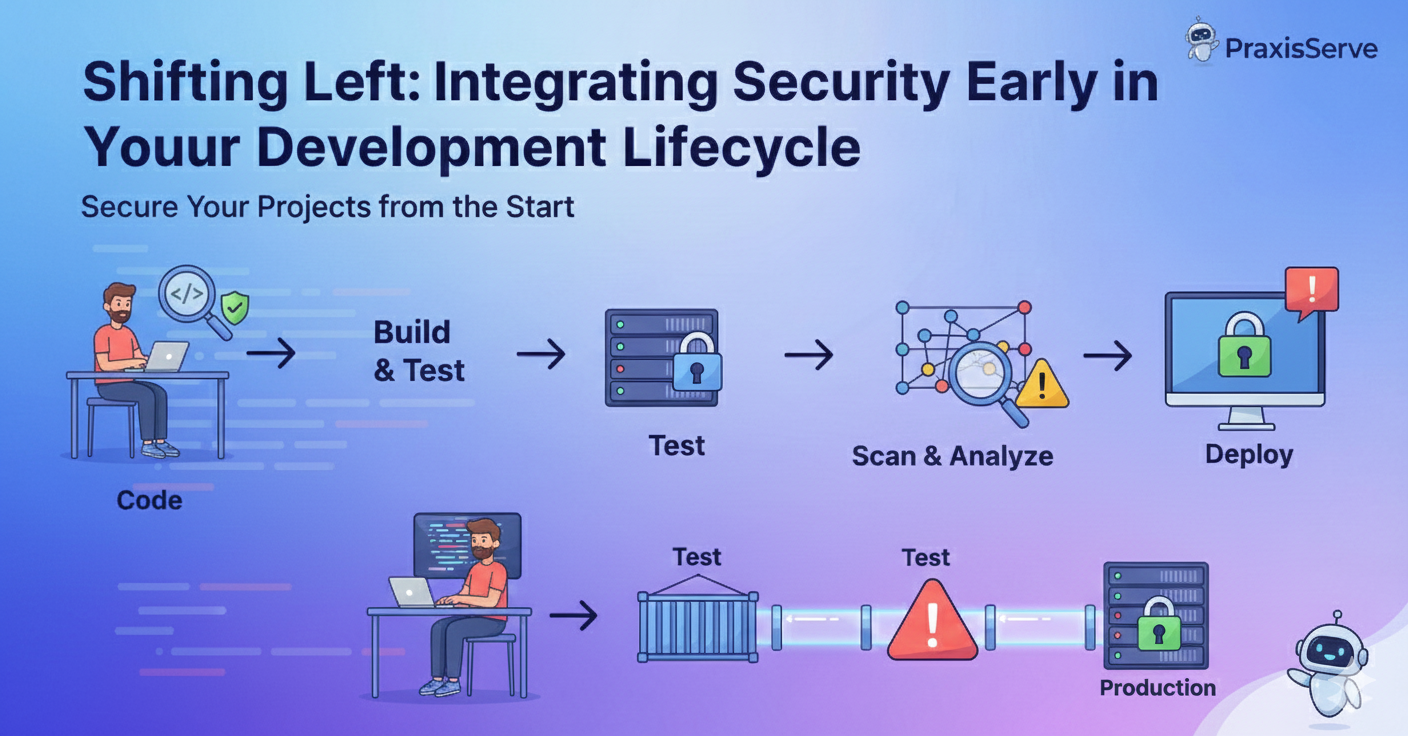
The concept of "Shift Left" on Security advocates for integrating security practices and testing into the earliest possible stages of the Software Development Life Cycle (SDLC). Instead of being a final gatekeeper, security becomes an ongoing, collaborative effort from planning to deployment.
Why "Shift Left" Matters for Small Teams
- Cost Efficiency: Finding and fixing a bug in the design or coding phase costs significantly less than finding and fixing it in production. This applies even more to security vulnerabilities.
- Faster Development Cycles: By catching issues early, you avoid costly rework and delays later on, keeping your CI/CD pipelines smooth.
- Enhanced Trust & Reputation: Proactive security builds stronger, more reliable applications, which directly translates to happier clients and a better industry reputation.
- Reduced Risk: Minimizing the attack surface from the start significantly lowers the likelihood of data breaches and other security incidents.
- Developer Empowerment: Developers learn to write more secure code from the outset, integrating security best practices into their daily habits.
Practical Ways to Shift Left on Security
1. Secure Design & Threat Modeling
Before writing any code, consider potential threats. Ask: "How could an attacker compromise this feature?" This helps you build security into the architecture itself.
Example: Discussing data encryption needs before setting up a database.
2. Static Application Security Testing (SAST)
Integrate tools into your CI/CD pipeline that analyze your code for security vulnerabilities *without* executing it. This catches common flaws like SQL injection or cross-site scripting (XSS) early.
Tools: SonarQube, GitHub CodeQL, Snyk Code.
3. Software Composition Analysis (SCA)
Most modern applications rely heavily on open-source libraries. SCA tools scan your dependencies for known vulnerabilities, ensuring you don't inherit security risks.
Tools: Snyk, Dependabot (built into GitHub), OWASP Dependency-Check.
4. Dynamic Application Security Testing (DAST)
While SAST checks code, DAST tests your running application for vulnerabilities by attacking it as a hacker would. This is typically done in staging environments.
Tools: OWASP ZAP, Burp Suite (professional edition).
5. Developer Security Training
Empower your team with knowledge. Regular training on secure coding practices (e.g., OWASP Top 10) helps developers prevent vulnerabilities from being introduced in the first place.
Strengthen Your Security Posture with PraxisServe
Implementing a robust "Shift Left" security strategy can seem daunting for small teams. PraxisServe specializes in helping freelancers and agencies integrate pragmatic security practices into their DevOps workflows.
From setting up automated security scans in your CI/CD pipeline to providing guidance on secure coding, we ensure your applications are built with security in mind, from the very first line of code.
Need Help with This?
Our team is ready to assist you with implementation and support.